Gaseous Laws and Ideal Gas Equation
Gaseous Laws and Ideal Gas Equation: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Gas Laws, Boyle's Law, Graphs Based on Boyle's Law, Isotherm in Graph, Charles' Law, Graphs Based on Charles' Law, Isobar in Graph, Absolute Zero Temperature, Gay-Lussac's Law, Graphs Based on Gay-Lussac's Law, etc.
Important Questions on Gaseous Laws and Ideal Gas Equation
What volume of oxygen gas measured at and 1 atm, is needed to burn completely 1L of propane gas measured under the same conditions?
In a closed flask of 5 litres, 1.0 g of is heated from 300 K to 600 K. Which statement is not correct?
A bubble of air is underwater at temperature and the pressure 1.5 bar. If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is and the pressure is 1.0 bar, what will happen to the volume of the bubble?
Cyclopropane and oxygen at partial pressures torr and torr respectively are mixed in a gas cylinder. What is the ratio of the number of moles of cyclopropane to the number of moles of oxygen (Assume no reaction).
The correct value of the gas constant is close to:
If are pressure, volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by
If are pressure, volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by
The density of the gaseous mixture in a vessel at 2.1 atmosphere and 310 K is 1.35 g/litre. If a small pin-hole is made on the wall of the vessel, through which gases effuse, then which of the following is the correct composition of the gases He and effusing out initially?
Internal energy of mol of hydrogen of temperature is equal to the internal energy of mol of helium at temperature . The value of is
At STP, litre of a gas weighs . The vapour density of gas is -
Consider one mole of a gas in a closed vessel fitted with a movable piston. At constant temperature , the pressure of the gas is increased gradually and the volume is noted. The resulting isotherm (not drawn to scale) is given below.
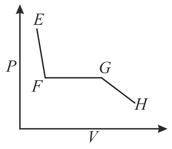
The correct plot (not drawn to scale) of the number of moles of the substance in gas phase $\left(n_{\mathrm{G}}\right)$ against $V$ or $P$ is:
Consider the chemical equilibrium inside a vessel fitted with a movable piston at temperature . The correct plot corresponding to volume change (assuming ideal gas behavior) is
A thermally insulated vessel is partitioned into two compartments by a fixed diathermal (heat conducting) wall and each compartment contains certain amount of ideal gas. The temperature, pressure, volume, number of moles, entropy of the gases in the first and second compartments are denoted by and , , respectively. Initially, and and the system evolves in time till thermal equilibrium is reached. The correct figure(s) depicting this spontaneous process, can be described as
A certain gaseous reaction, carried out in an insulated sealed container results in an increase in temperature from to , with the pressure remaining constant. The correct equation that describes the reaction is:
The temperature of a given mass of a gas is increased from to at constant pressure. The volume of the gas is increased
A balloon filled with an air sample occupies volume at On lowering the temperature to the volume decreases to The temperature is? [Assume P constant]
When a perfect gas at is heated, at a constant pressure, to a final temperature of . then the volume of the gas increases to_________ times the original.
Pressure of ideal gas at is When of another gas is introduced in the same vessel at same temperature, the pressure become The correct relationship between molar mass of and is
For formation of of ammonia gas, what volumes of hydrogen gas and nitrogen gas, respectively, are required at conditions?
The graph between P and T according to Gay lussac's law is a
